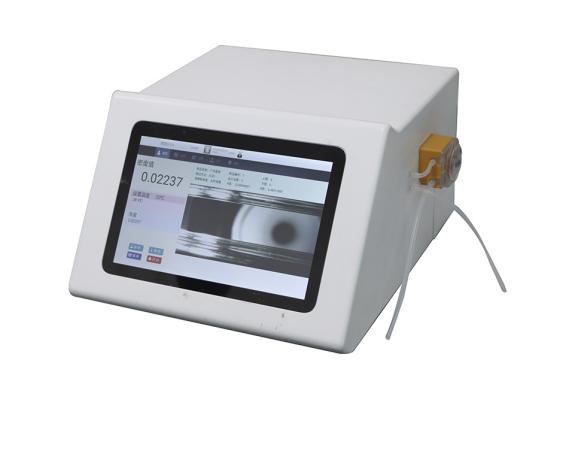
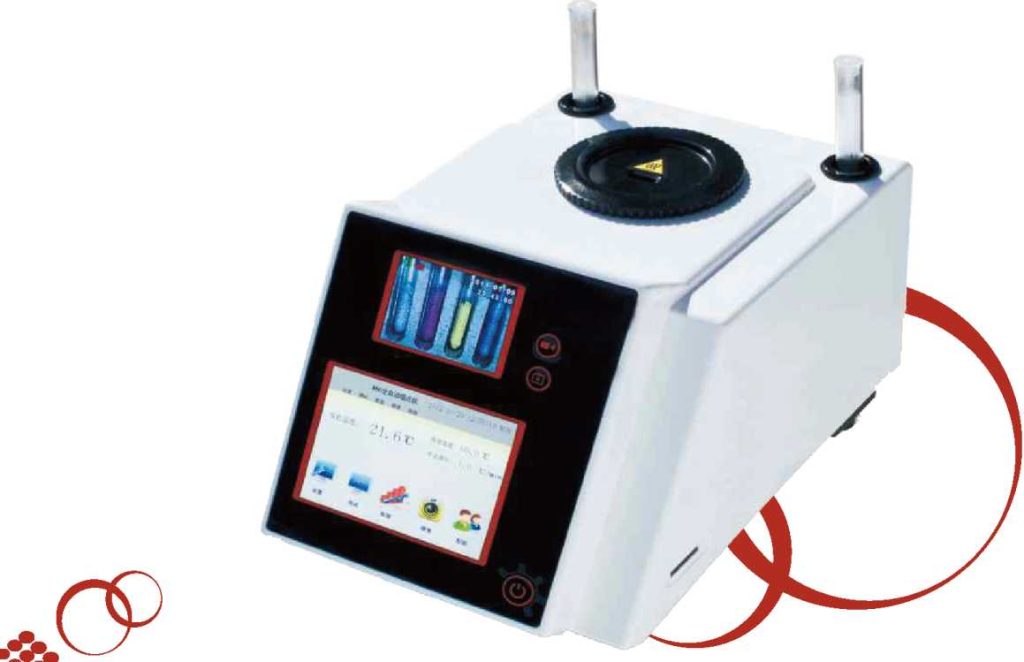
In various industries where precise measurements of liquid properties are essential, the automatic refractometer emerges as an invaluable tool. This sophisticated instrument plays a pivotal role in quality control, research, and development by accurately determining the refractive index of substances. In this article, we delve into the workings of the automatic refractometer, its applications, and a comprehensive guide on how to use it effectively.

What is an Automatic Refractometer?
An automatic refractometer is a modern marvel that measures the refractive index of a liquid or substance. The refractive index is a measure of how much light is bent or refracted as it passes through a medium, compared to its speed in a vacuum. This property is influenced by the concentration of dissolved solids within the liquid, making the refractometer an essential tool in assessing the composition of various substances.
The automatic refractometer differentiates itself from its manual counterpart by its advanced features. It employs a combination of light sources, prisms, detectors, and digital displays to streamline the measurement process. This automation reduces human error, enhances precision, and accelerates the measurement procedure, thereby increasing overall productivity.
How Does an Automatic Refractometer Work?
The operation of an automatic refractometer is based on the principles of light refraction. When a sample liquid is placed on the measurement surface, light from a source is directed through the sample and onto a prism. As the light exits the prism, it is detected by a sensor. The angle at which the light is bent, known as the angle of refraction, is a direct indicator of the refractive index of the liquid. This refractive index can, in turn, be correlated to properties like concentration or purity, providing valuable insights into the sample’s composition.
To ensure accurate readings, many automatic refractometers are equipped with temperature compensation mechanisms. Since temperature can influence the refractive index, this feature adjusts the measurement to a standard temperature, guaranteeing consistent results regardless of temperature variations.

What are the Applications of an Automatic Refractometer?
The applications of automatic refractometers span diverse industries, where precision measurements are essential for product quality, process control, and research. Some prominent applications include:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Automatic refractometers are employed to measure sugar content in juices, soft drinks, and syrups. This ensures that products meet desired sweetness levels and taste profiles.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: These instruments play a crucial role in measuring the concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredients in solutions, contributing to the consistency and efficacy of medicinal products.
- Chemical Industry: Automatic refractometers aid in determining the concentration of various chemicals in solutions, facilitating precise formulation and analysis.
- Automotive Industry: They are used to assess the concentration of antifreeze and coolants, ensuring engine protection and optimal performance.
- Cosmetics Industry: Refractometers measure the concentration of components in cosmetic products, enabling manufacturers to maintain product consistency and performance.
- Research and Laboratory Settings: In scientific research, automatic refractometers help study the refractive properties of materials, contributing to advancements in various fields.

How to Use an Automatic Refractometer Effectively? Here is A Step-by-Step Guide:
- Step 1: Preparation
Ensure the refractometer is clean and calibrated as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Power on the refractometer and allow it to stabilize, if required.
- Step 2: Sample Collection and Handling
Collect a representative sample of the liquid to be measured.
If the sample temperature differs from the instrument’s temperature, use a temperature-controlled sample holder or wait for equilibration.
- Step 3: Measurement
Open the sample cover or well on the refractometer.
Place a small drop of the liquid on the measurement surface, avoiding air bubbles.
Gently close the sample cover for proper contact between the liquid and the measurement surface.
- Step 4: Reading the Results
Look through the eyepiece or view the digital display for the refractive index or concentration reading.
Some automatic refractometers might record and store results automatically.
- Step 5: Cleaning and Maintenance
After measurement, clean the measurement surface meticulously to prevent contamination between samples.
Follow routine maintenance procedures recommended by the automatic refractometer manufacturer.
- Step 6: Shutdown
Turn off the refractometer and store it in a clean, dry environment.
- Step 7: Troubleshooting and Calibration
Refer to the user manual of an automatic refractometer for troubleshooting guidance if encountering inconsistent readings.
Regularly calibrate the refractometer using appropriate standards for sustained accuracy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the automatic refractometer serves as a cornerstone in industries reliant on precise measurements. Its automation, speed, and accuracy empower professionals to assess the composition of liquids with unparalleled precision. Whether in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, or chemical sectors, the automatic refractometer’s versatility and convenience make it an indispensable asset in modern quality control and research endeavors. By following the provided guide, users can harness the potential of this instrument effectively and confidently.