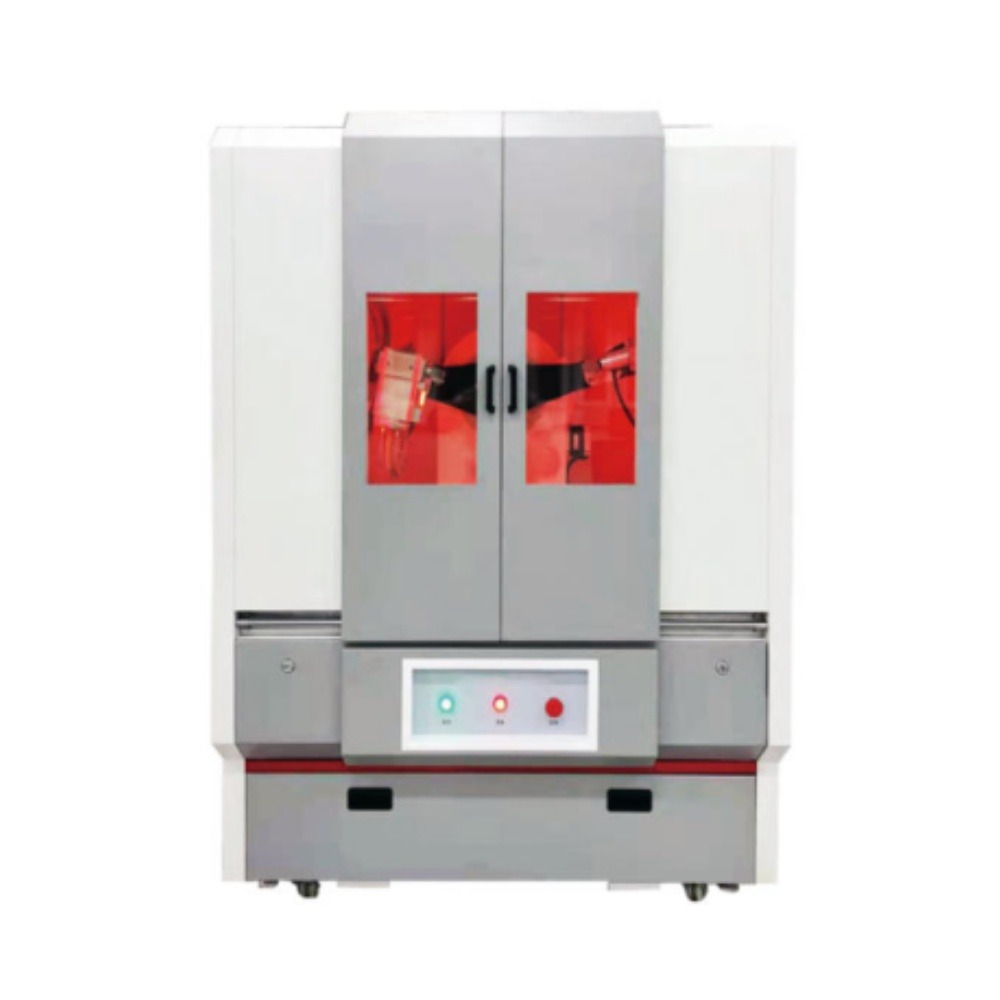
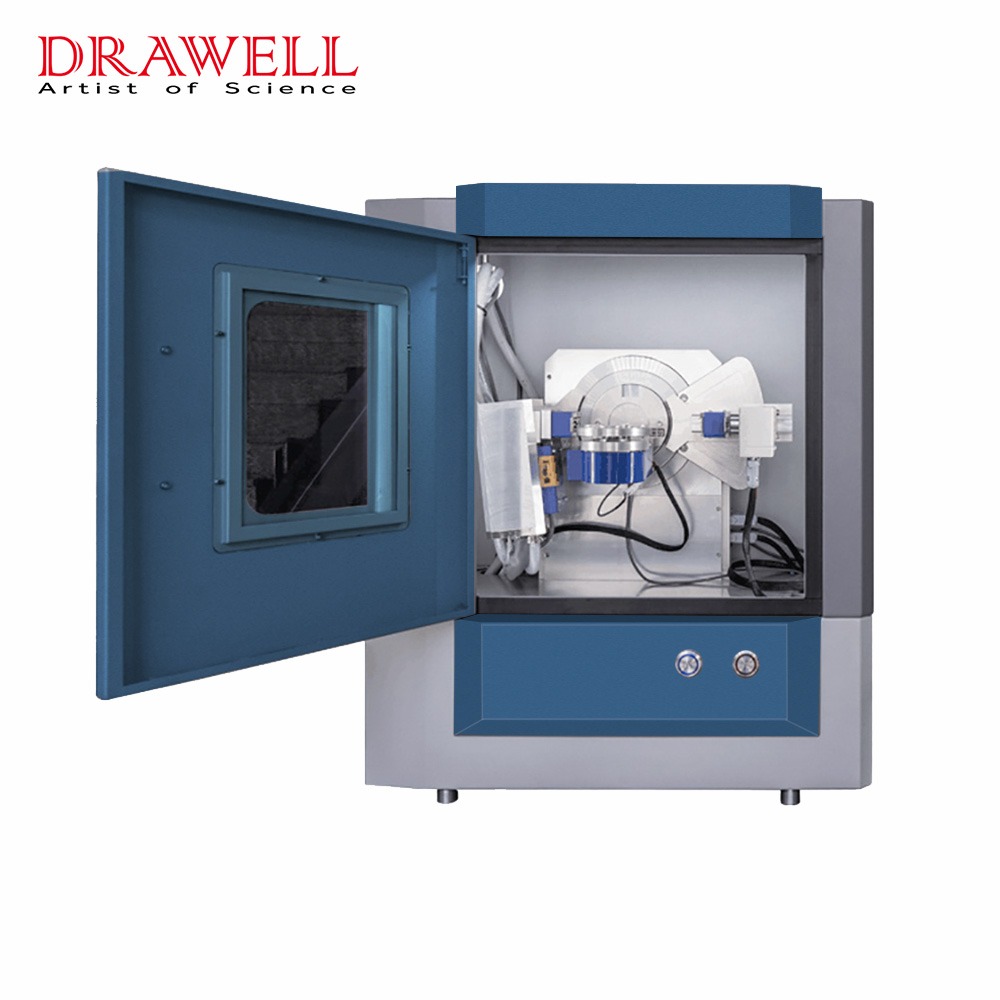
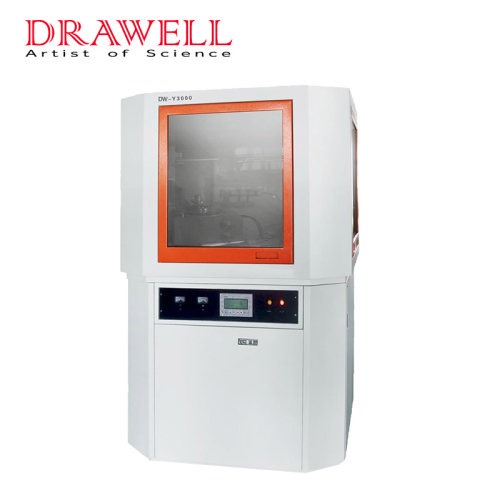
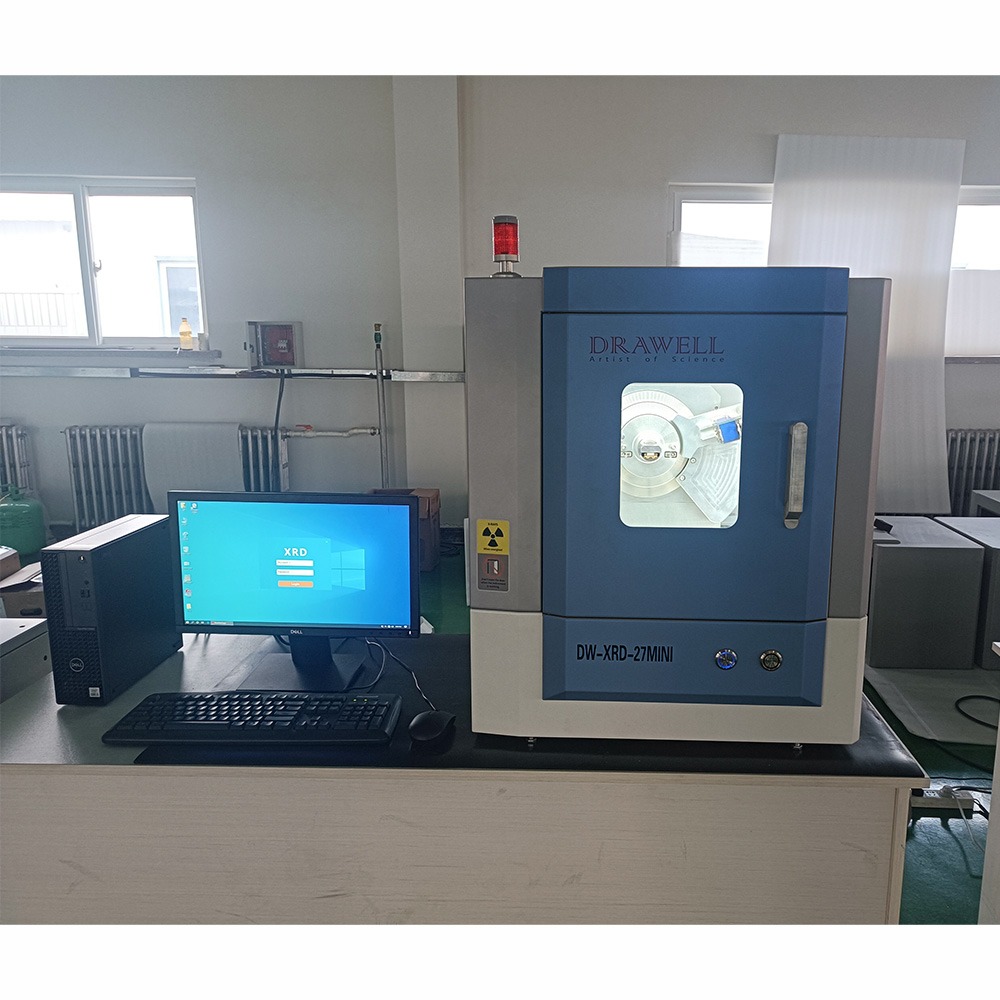
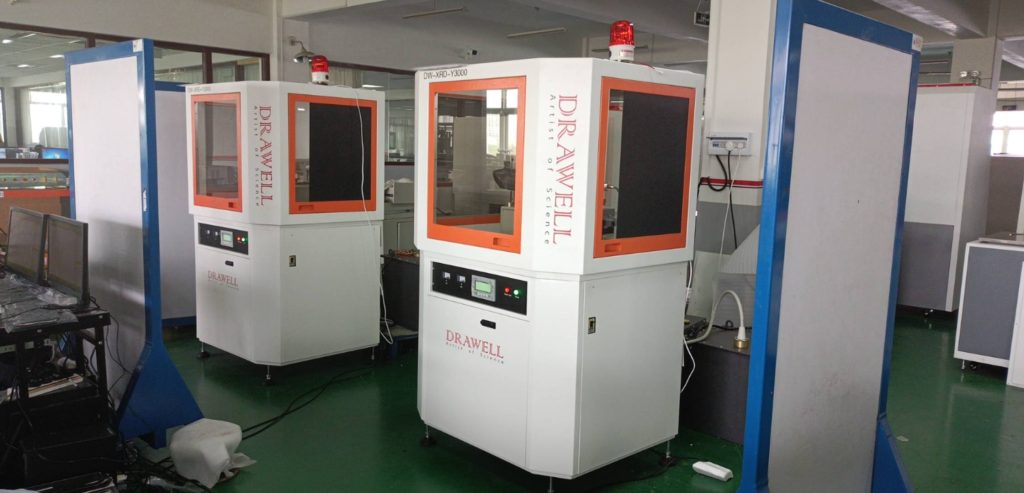
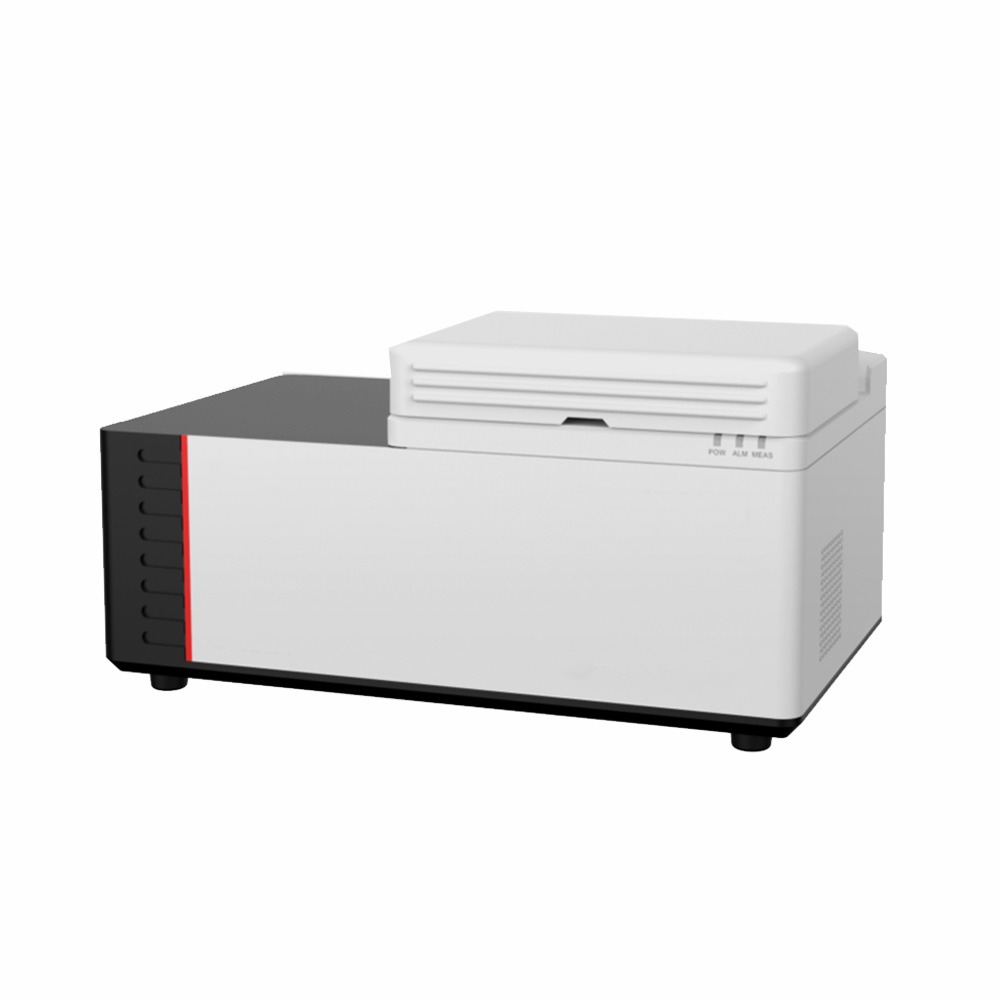
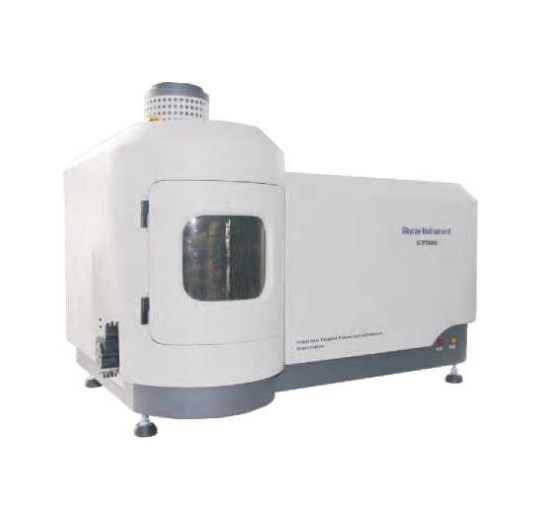
X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD)
Features | Advantages | Application | How does work | Image | Why Choose Drawell | Other Products
An X-ray diffractometer, often referred to as XRD (X-ray diffraction) instrument, is a scientific device used to analyze the crystalline structure of materials by measuring the diffraction of X-rays.
The vast majority of solid materials are crystals or quasicrystals, which can produce characteristic diffraction of X-rays. By recording these diffractions in a proper way, different patterns of X-ray diffraction patterns can be obtained. It can be said that the X-ray diffraction pattern of each substance carries a wealth of information about the structure of the substance. By analyzing these patterns, the structure of the sample can be studied and determined. “Structure” here includes the elemental composition, composition, structure, organization, structure, state, and other meanings of material materials.
With the continuous advancement of technology, XRD analysis has now been widely used in product inspection, raw material quality standards, and production processes.
Features of X-Ray Diffractometer
- A wide range of applications, meeting the needs of scholars and researchers in various fields.
- High-precision diffraction angle measurement system to obtain more accurate measurement results.
- Highly stable X-ray generator control system to obtain more stable repeat measurement accuracy.
- Non-destructive, non-destructive analysis method.
- Easy to prepare samples.

Advantages of X-Ray Diffraction
- High-precision detection technology for rapid detection of unknown materials.
- Small sample detection amount, suitable for research in most production processes.
- Equipped with fast and accurate analysis software, automatic analysis of test results, easy operation for technicians who are not proficient in XRD.
- Non-destructive operation on samples during testing, no damage to samples.
- Not only can the composition, characteristics and structure of different elements be detected, but also the characteristics of different materials can be quickly detected, and XRD detection technology can be widely used in multiple chemical industry fields.
Applications of X-Ray Diffractometer
Because the X-ray diffraction method has the advantages of no damage to samples, no pollution, fast measurement accuracy, and a large amount of information about crystal integrity, the X-ray diffraction technology is used in cement building materials, cotton, rock minerals, scientific research, aviation, It has a wide range of applications in materials production and other fields.

How Does X-Ray Diffraction Work?
X-ray diffractometers are most widely used to research the phase and crystal structure of matter. When analyzing materials with XRD, each chemical molecule or phase has a unique diffraction pattern.
XRD testing focuses an X-ray beam onto the surface of a metal sample to determine the composition and structure of certain elements in the sample, such as average grain size, crystal defects, orientation, and strain.
The X-ray beam is scattered by the sample during the diffraction process. This produces an interference pattern that is unique to each material and provides information about the sample’s structure. Determining the diffraction pattern requires mathematical calculations and physical measurements.
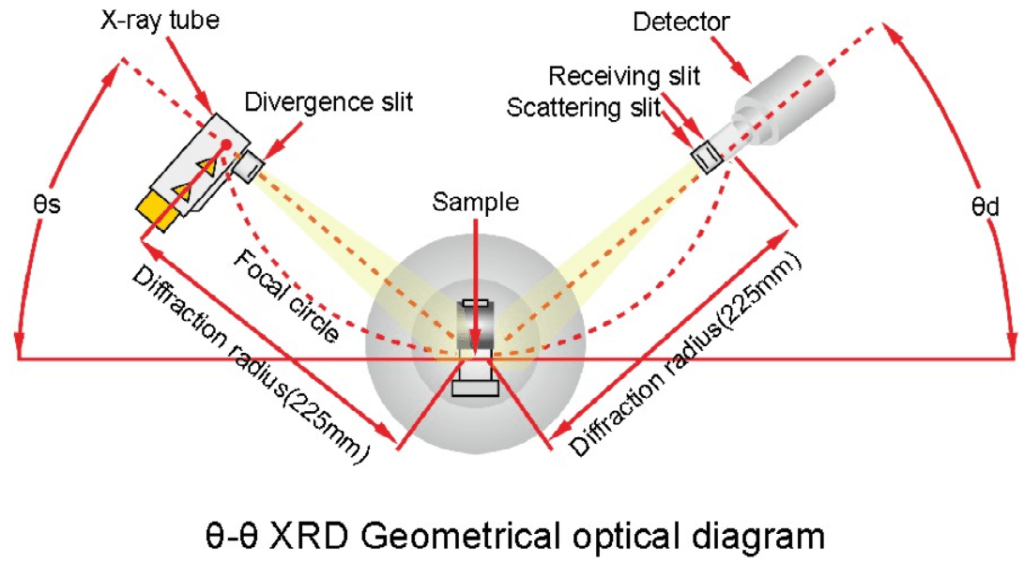
The resulting interference pattern is then analyzed to determine the crystal structure of the sample and provide information about the composition and properties of the material. Using this method, the presence of different elements and phases in a material can be determined and their relative quantities measured.
XRD Display
Why Choose Us for XRD?
“Multiple suppliers” have always been an issue in the procurement process. Drawell as a one-stop laboratory equipment and scientific instruments supplier, can perfectly solve this problem. In addition to manufacturing our own equipment, we also represent other laboratory equipment. Our product lines are rich and diverse at competitive prices. Provide one-stop service to customers.
User Training – Training by Drawell skilled engineers about installation, debug tests, technical services, etc. It can happen in our factory in China, or at the site in the customers’ country. Cost depends on where and when the training happens.
To discuss the problem and get it resolved, online chats, real-time video calls, and remote guidance. For the after-sales stage, our online technical guidance is free and ready forever.
1 year free official warranty, including repairing quality-damaged parts, and offering replacements of selected parts (shipping cost is extra). 5% of the product price is charged for extending the warranty before the end of the official warranty.