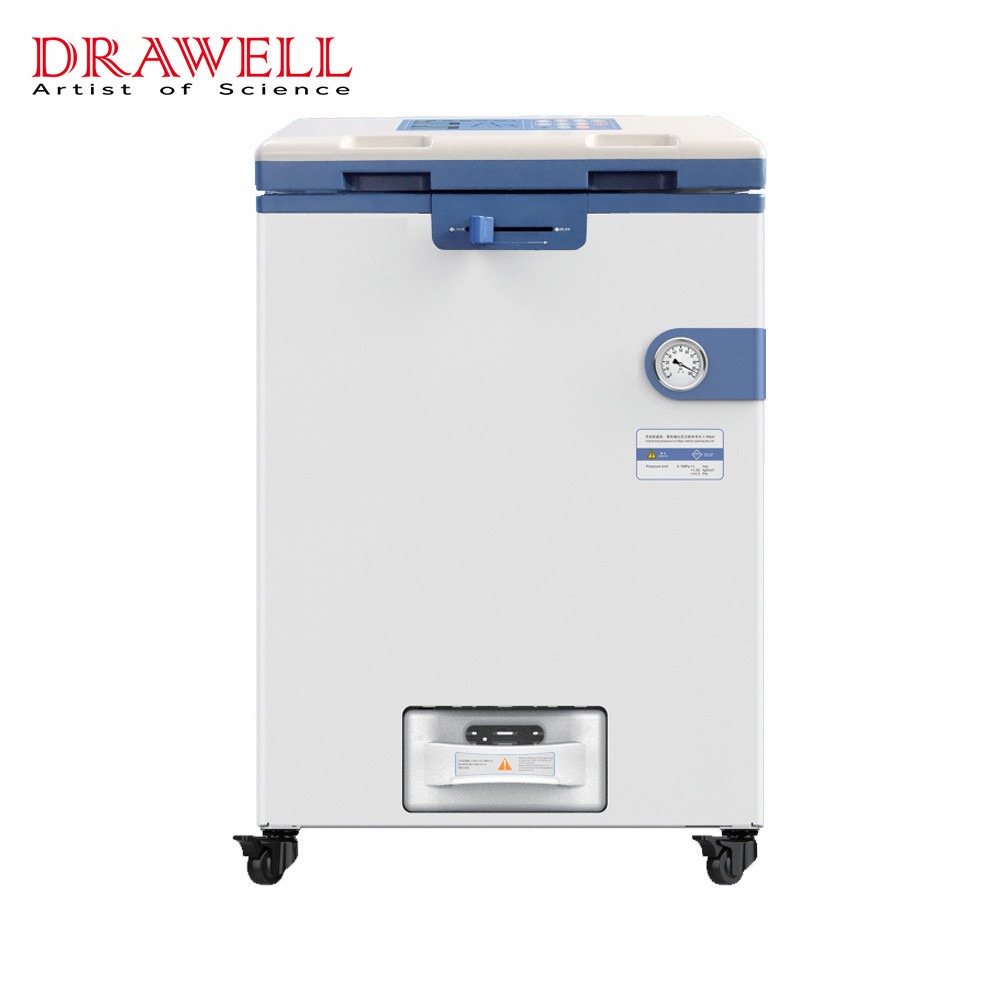
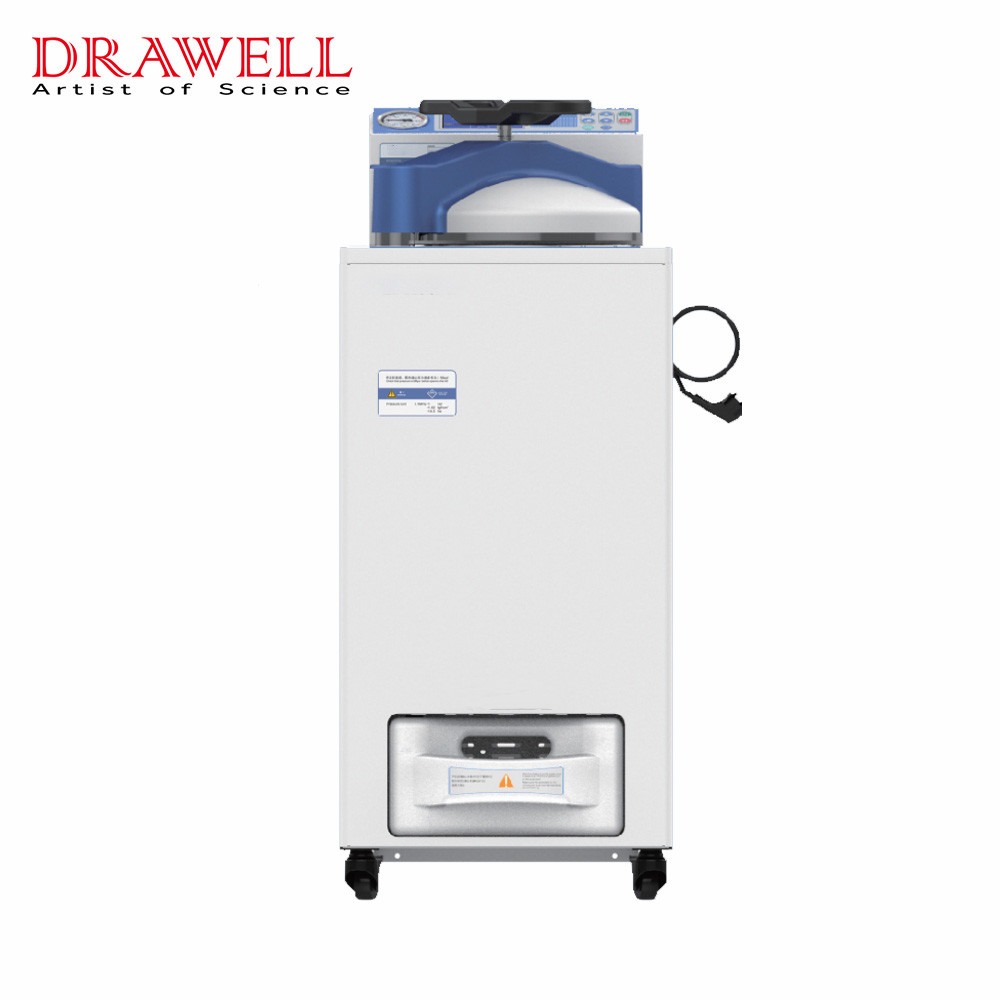
In the realm of surgical procedures, ensuring the utmost cleanliness and sterility of instruments is paramount to patient safety and successful outcomes. Precision sterilization methods play a pivotal role in preventing infections and reducing the risk of complications. Among the array of sterilization techniques, steam autoclaves stand out as a reliable and efficient solution for achieving surgical instrument sterility. In this article, we delve into the significance of sterilization in surgical settings, explore the functionality of steam autoclaves, and discuss best practices for their utilization.
Understanding Sterilization in Surgical Settings
Sterilization is the process of eliminating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from surfaces, instruments, and environments. In a surgical setting, sterilization of instruments and equipment is essential to prevent surgical site infections (SSIs). Inadequate sterilization can lead to postoperative infections, prolonged hospital stays, compromised patient recovery, and even fatalities.
Methods of Sterilization Used in Healthcare Settings
In healthcare settings, various methods of sterilization are employed to ensure the elimination of microorganisms and prevent the transmission of infections. Some of the most common methods include:
- Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving): This method utilizes high-pressure steam to achieve sterilization. Autoclaves are widely used for sterilizing medical instruments, equipment, and surgical supplies. Steam penetrates materials effectively, and the high temperature (typically around 121°C to 134°C) ensures the destruction of bacteria, viruses, and spores.
- Ethylene Oxide (ETO) Sterilization: Ethylene oxide gas is used to sterilize heat-sensitive medical devices and supplies that cannot withstand high temperatures. ETO penetrates packaging and materials, killing microorganisms by damaging their DNA. This method requires careful handling due to the toxic nature of ethylene oxide gas.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Dry heat sterilization involves heating items at high temperatures (usually between 160°C to 190°C) for a specified period. It is suitable for items that are sensitive to moisture, such as powders, oils, and certain types of glassware. Dry heat sterilization is effective against bacteria, fungi, and viruses but may require longer exposure times compared to steam sterilization.
- Chemical Sterilization: Chemical sterilants such as hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, and glutaraldehyde are used to sterilize heat-sensitive instruments and equipment. These chemicals kill microorganisms by disrupting their cellular structures. The sterilization process may involve immersion, spraying, or gas sterilization chambers.
- Radiation Sterilization: Ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays and electron beams, is used to sterilize disposable medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and packaging materials. Radiation damages the DNA of microorganisms, preventing their replication and causing their death. This method is particularly suitable for items that cannot withstand high temperatures or chemical exposure.
- Plasma Sterilization: Plasma sterilization uses low-temperature plasma to sterilize heat-sensitive medical devices and instruments. Plasma generates free radicals and reactive species that disrupt microbial structures and deactivate enzymes, achieving sterilization without damaging delicate materials.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Sterilization: UV light with a specific wavelength (around 254 nm) is used to sterilize surfaces, air, and water by damaging the DNA of microorganisms, preventing their replication. UV sterilization is often used in biosafety cabinets, water treatment systems, and air purification units.
Each sterilization method has its advantages, limitations, and applications, and healthcare facilities select the most appropriate method based on factors such as the type of material to be sterilized, the level of microbial contamination, and the required sterility assurance level. As steam autoclave sterilization is considered the most effective method for sterilizing surgical instruments, let’s get to know more about it.

What are the Steam Autoclaves?
Steam autoclaves are highly effective devices used for sterilizing medical instruments, equipment, and supplies in various healthcare settings. These autoclaves operate on the principle that moist heat, in the form of pressurized steam, can rapidly penetrate materials and effectively kill microorganisms by denaturing their proteins and disrupting their cellular structures. They are essential tools in ensuring patient safety by preventing the transmission of infections during medical procedures.

Key Features and Components of Steam Autoclaves Include:
- Chamber: The chamber is the main compartment where items to be sterilized are placed. It is typically made of stainless steel to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
- Steam Generator: Steam is generated by a dedicated steam generator within the autoclave. This steam is then injected into the chamber to create the necessary sterilizing environment.
- Pressure Vessel: The pressure vessel is designed to withstand high pressure during the sterilization process. It ensures that steam remains at the desired pressure level to achieve effective sterilization.
- Control System: Autoclaves are equipped with control systems that regulate temperature, pressure, and sterilization cycle times. These systems ensure precise control over the sterilization process for optimal results.
- Safety Features: Steam autoclaves are equipped with safety features such as pressure relief valves, temperature sensors, and interlocking mechanisms to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety.
- Drying Cycle: Many autoclaves include a drying cycle to remove excess moisture from sterilized items, preventing corrosion and maintaining their quality.
Steam autoclaves also offer several advantages:
- Firstly, steam is highly effective in killing a wide range of microorganisms, including resilient spores, making it one of the most reliable sterilization methods available.
- Secondly, steam autoclaves are environmentally friendly, as they utilize water as the sterilizing agent, eliminating the need for potentially harmful chemicals.
- Additionally, steam sterilization is fast and efficient, with most cycles completing within a matter of minutes.
They are essential tools for maintaining aseptic conditions in healthcare facilities and ensuring patient safety during medical procedures.
How to Use Steam Autoclaves for Surgical Instruments?
Using steam autoclaves for sterilizing surgical instruments requires careful attention to detail and adherence to proper procedures to ensure effective sterilization and maintain instrument integrity. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use steam autoclaves for surgical instruments:
- Preparation:
- Inspect the surgical instruments for cleanliness and functionality. Remove any visible debris or organic material.
- Ensure that the instruments are disassembled, if necessary, to allow steam penetration and thorough sterilization.
- Place the instruments in sterilization trays or pouches designed for autoclaving. Arrange them in a manner that promotes even steam distribution and proper sterilization.
2. Loading:
- Open the autoclave door and carefully load the sterilization trays or pouches containing the surgical instruments.
- Avoid overcrowding the autoclave chamber to allow adequate steam circulation around each instrument.
3. Water Filling:
- Fill the autoclave’s water reservoir with distilled or deionized water according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The water level should be sufficient to generate steam throughout the sterilization cycle.
4. Programming:
- Set the appropriate sterilization parameters on the autoclave control panel, including temperature, pressure, and sterilization cycle time.
- Select the sterilization cycle that is recommended for the type of instruments being sterilized. Common cycles include gravity displacement or pre-vacuum cycles.
5. Sealing:
- Close the autoclave door securely, ensuring that it is tightly sealed to prevent steam leakage during the sterilization process.
6. Initiating Sterilization Cycle:
- Start the sterilization cycle according to the programmed parameters. The autoclave will generate steam and raise the temperature and pressure to levels necessary for sterilization.
- Monitor the autoclave throughout the sterilization cycle to ensure that it operates within the specified parameters and troubleshoot any issues if necessary.
7. Cooling:
- After the sterilization phase is complete, the autoclave will gradually release pressure and cool down. Allow the autoclave to complete the cooling cycle before opening the door.
8. Unloading:
- Once the autoclave has cooled down, open the door carefully to avoid steam burns.
- Remove the sterilization trays or pouches containing the sterilized surgical instruments from the autoclave chamber.
- Inspect the instruments for signs of moisture or condensation. If present, allow the instruments to dry completely before use or storage.
9. Documentation:
- Record the sterilization cycle parameters, including temperature, pressure, and cycle duration, in the sterilization log.
- Label the sterilized instruments with the sterilization date and batch number for traceability.
10. Storage:
- Store the sterilized instruments in a clean, dry environment until they are needed for use in surgical procedures.
By following these steps carefully and consistently, healthcare professionals can effectively utilize steam autoclaves to ensure the sterility of surgical instruments, contributing to patient safety and infection prevention in healthcare settings.
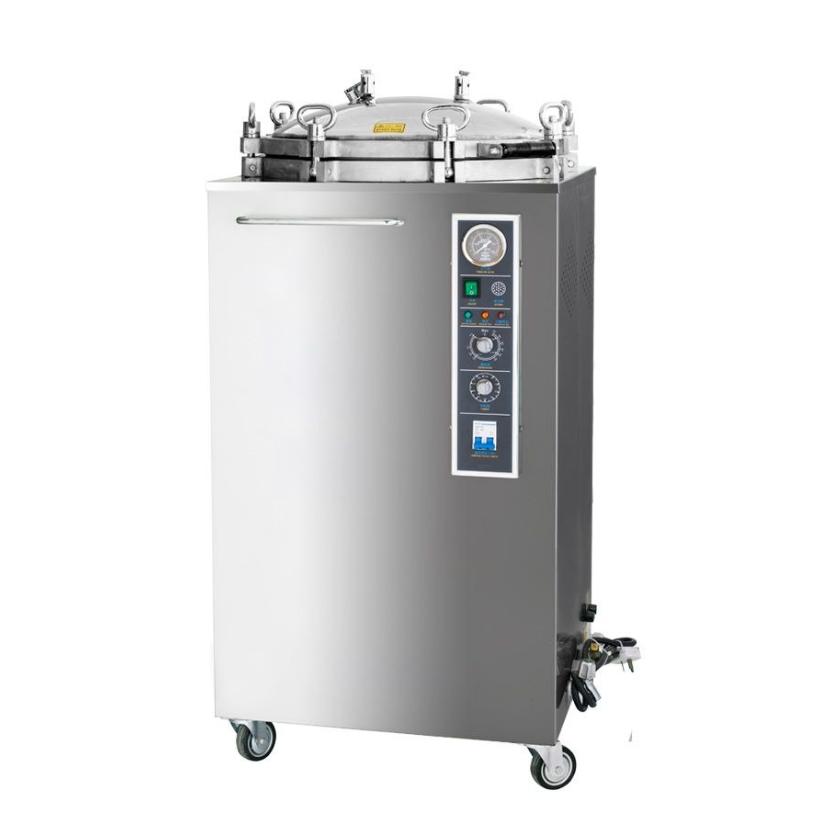

Conclusion
In conclusion, precision sterilization is indispensable in surgical settings to safeguard patient health and prevent infections. Steam autoclaves offer a reliable and efficient solution for achieving surgical instrument sterility, thanks to their ability to harness the power of pressurized steam. By partnering with a trusted steam autoclave supplier – Drawell, healthcare facilities can confidently embrace steam autoclaves as indispensable tools in their infection control arsenal and ensure the safety and well-being of patients undergoing surgical procedures.






