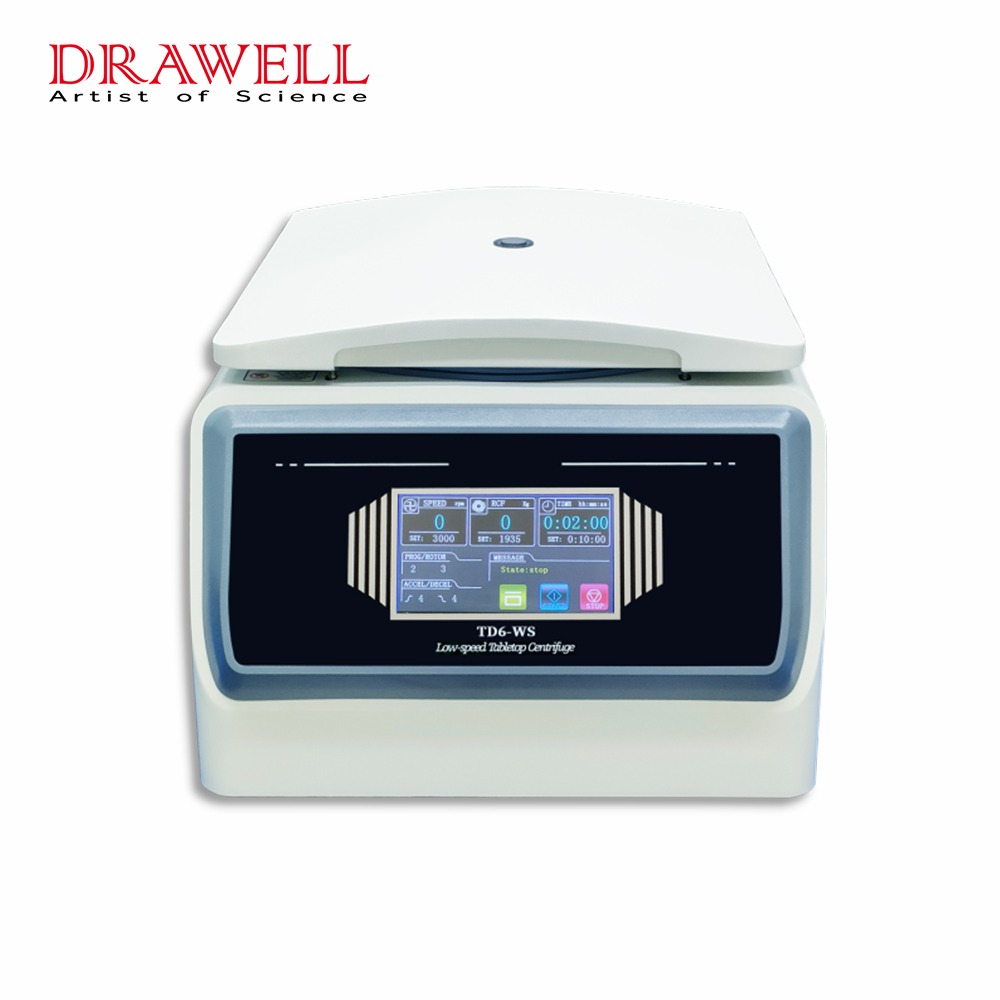
Blood banks are the beating heart of the healthcare system, providing life-saving transfusions to patients in critical need. But before that precious blood reaches a recipient, it undergoes a vital transformation within the walls of the blood bank, one orchestrated by a seemingly unassuming machine: the centrifuges.

Why Using Centrifuge in Blood?
Imagine blood as a bustling metropolis. Red blood cells, the workhorses carrying oxygen, are like the bustling commuters. Platelets, the tiny traffic wardens, keep things flowing smoothly. Plasma, the watery infrastructure, acts as the lifeblood of the system. But in its natural state, these components mingle freely, making targeted treatments difficult.
Filtration, while effective for some tasks, struggles to differentiate these components based on their subtle density differences. This is where the centrifuge steps in, wielding the power of centrifugal force to create a “molecular metropolis.”
How Centrifuge Works in Blood? Spinning for Separation
Imagine placing our bustling city on a merry-go-round and spinning it faster and faster. The heavier red blood cells, like skyscrapers, stay closer to the center, while the lighter platelets and plasma, like nimble pedestrians, are flung outwards. This is the essence of centrifugation: separating components based on their density and the applied force.
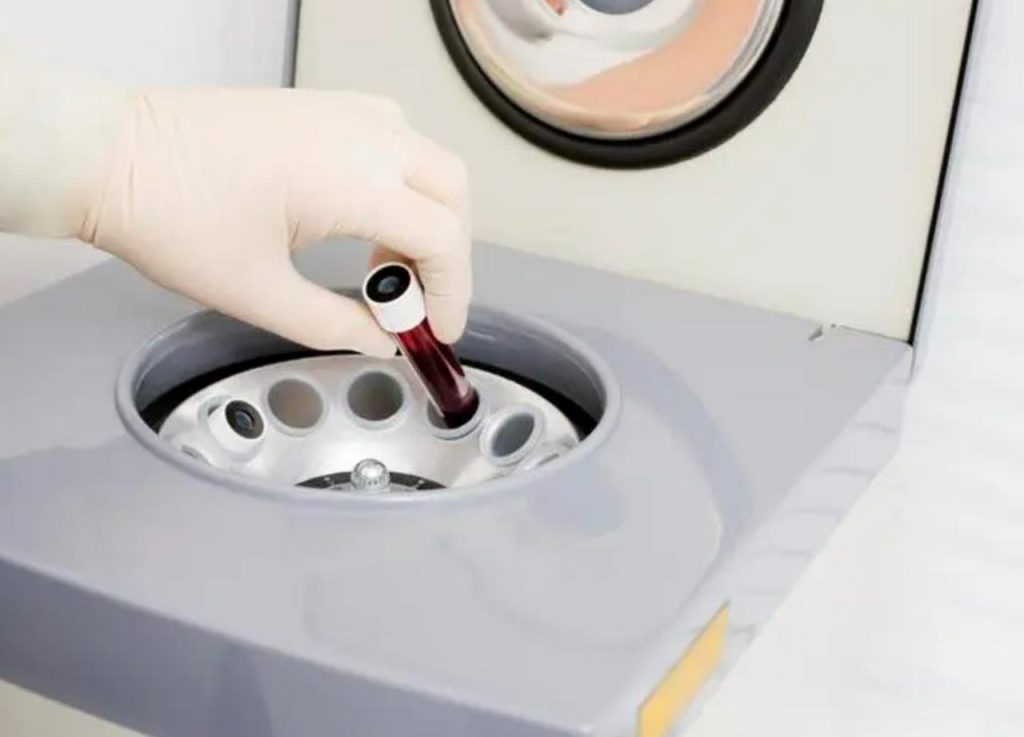
What are the Specific Applications of Centrifuges in Blood Banks?
Blood bank centrifuges perform a variety of crucial tasks:
- Plasma Separation: Isolating plasma for use in treating burn victims, shock patients, and those with clotting disorders.
- Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Preparation: Concentrating platelets for use in wound healing and promoting tissue regeneration.
- Red Blood Cell (RBC) Packing: Concentrating red blood cells for transfusions, maximizing the oxygen-carrying capacity in a smaller volume.
- ABO/Rh Typing: Separating plasma and red blood cells to determine blood compatibility for safe transfusions.
- Viral Testing: Isolating plasma for sensitive tests to detect viruses like HIV and Hepatitis.

What are the Characteristics of Blood Bank Centrifuges?
Beyond the core principles of centrifugation, blood bank centrifuges possess unique features tailored to meet the specific demands of blood processing:
1. Temperature Control:
- Refrigeration: Maintaining a cool environment (typically 4-10°C) is crucial for preserving the integrity of blood components, especially platelets and white blood cells, which are sensitive to temperature changes. This can be achieved through built-in refrigeration units or external cooling systems.
- Temperature Monitoring: Constant monitoring of the internal temperature throughout the centrifugation process ensures optimal conditions and adherence to quality control standards.
2. Rotors and Adapters:
- Versatility: Blood bank centrifuges often have multiple rotors and adapters to accommodate different types of blood bags, tubes, and other containers. This allows for processing a variety of blood components and performing diverse applications.
- Safety and Balance: Rotors are designed to ensure balanced loading and prevent imbalances that could damage the centrifuge or compromise sample integrity. They may also have features like biocontainment lids to minimize the risk of spills and aerosolization during centrifugation.
3. Programmable Operation:
- Pre-set Protocols: Many blood bank centrifuges come with pre-programmed protocols for specific applications, like plasma separation, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) preparation, or red blood cell (RBC) packing. This simplifies operation and ensures consistency in results.
- Customizable settings: Some models allow for customization of speed, time, and g-force parameters to accommodate unique requirements or specific test protocols.
4. Additional Features:
- Smooth Operation: Minimizing vibrations and noise is essential for protecting delicate blood cells from shear stress and maintaining a pleasant working environment.
- Easy Cleaning and Disinfection: Blood bank centrifuges must be easy to clean and disinfect thoroughly after each use to prevent contamination and cross-contamination between samples. This may involve features like smooth, wipe-down surfaces or detachable rotors.
- Safety Interlocks: Built-in safety features, such as automatic door locks and imbalance detection systems, prevent accidents and protect users from potential harm.
- Data Logging and Traceability: Some advanced models offer data logging features that record run parameters and other information, aiding in quality control and traceability of samples.
Overall, the specific characteristics of blood bank centrifuges prioritize:
- Temperature control: To preserve blood component integrity.
- Versatility: To handle various blood containers and applications.
- Safety: To protect both samples and users.
- Ease of use and maintenance: To streamline workflow and maintain sterility.

Common Questions and Answers about Centrifuges in Blood Banks:
1. What types of centrifuges are used in blood banks?
There are two main types:
- Benchtop centrifuges: Smaller and more compact, used for routine tasks like ABO/Rh typing and plasma separation.
- Floor centrifuges: Larger and more powerful, used for high-volume processing, preparing platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and red blood cell (RBC) packing.
2. How often are centrifuges cleaned and maintained?
After every use, they undergo rigorous cleaning and disinfection protocols to prevent contamination. Regular maintenance checks and service are also essential to ensure optimal performance and safety.
3. Do different blood components require different centrifugation settings?
Yes, each component has varying density and separation requirements. Specific protocols for speed, time, and g-force are set for each application (e.g., plasma separation vs. PRP preparation). Many centrifuges offer pre-programmed settings for these tasks.
4. Are centrifuges used safely in blood banks?
Safety is paramount, and blood bank centrifuges have built-in safeguards:
- Door locks: Prevent access while the rotor is spinning.
- Imbalance detection: Stops the centrifuge if an imbalance is detected, protecting the machine and samples.
- Biocontainment lids: Minimize the risk of spills and aerosolization during centrifugation.
5. Can centrifugation damage blood cells?
Yes, excessive speed or time can damage delicate blood cells like platelets. Therefore, using appropriate settings and maintaining the centrifuge properly is crucial.
Conclusion
In the quiet hum of the blood bank centrifuge lies a silent revolution. This seemingly simple machine, with its whirling rotors and layered tubes, orchestrates a dance of separation, transforming a single unit of blood into a spectrum of life-saving components. Each spin yields a symphony of red cells, platelets, and plasma, poised to mend shattered lives and bolster fragile bodies.
The centrifuge’s impact extends far beyond the tangible separation it achieves. It expands the reach of a single donation, maximizing its potential to heal. It unlocks the doors to specialized therapies, offering targeted solutions for unique medical challenges. It fuels the machinery of research, propelling scientists towards ever-greater understanding of the intricate tapestry of human blood. The centrifuge is more than just a tool; it is the lifeblood of separation, the silent hero in the quiet drama of saving lives, one spin at a time.