Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are the first line of defense in laboratories and healthcare facilities against the potential hazards of working with biological materials. These specialized containment devices are intended to provide a safe and sterile environment for researchers, laboratory personnel, and the surrounding environment. In this article, we focus on the topic of biosafety cabinet use, exploring the key practices of biosafety cabinets to guarantee both safety and efficacy in various laboratory settings and the diverse uses of biosafety cabinets across various industries.

Best Practices for Biosafety Cabinet Use
Understanding Biosafety Cabinets
Biosafety cabinets are specialized containment devices that serve as a barrier between the user and the biological agents under consideration. They are divided into three classes based on the level of protection they provide (Class I, Class II, and Class III), with each class serving a different purpose and accommodating different types of research.
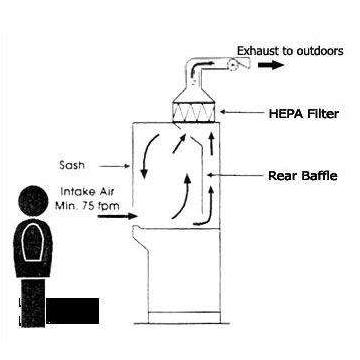
Class I Biosafety Cabinets
When dealing with low to moderate-risk agents.
Personnel and environmental protection are provided, but no product protection is provided.
Suitable for applications such as sample weighing and non-volatile chemical handling.
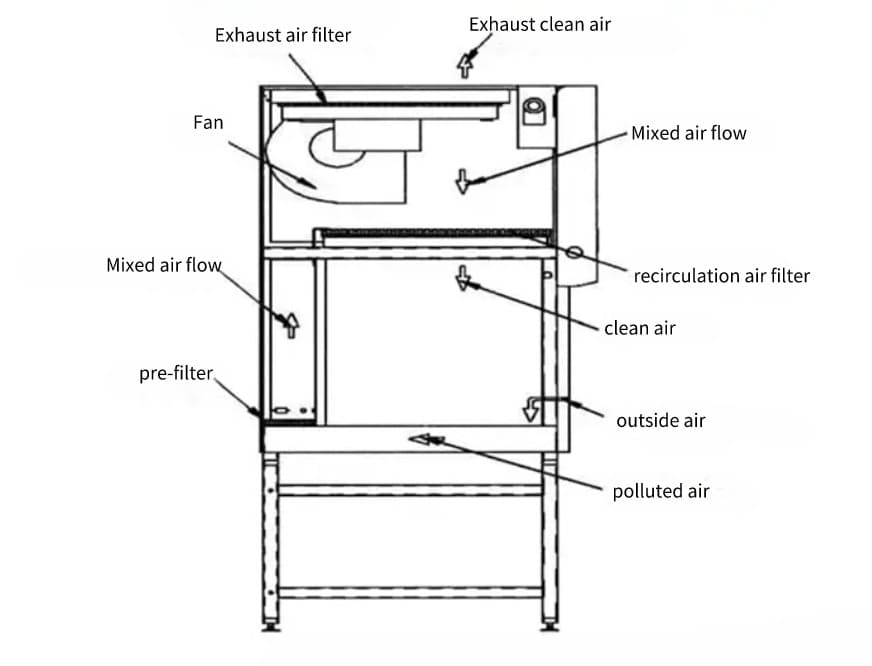
Class II Biosafety Cabinets
Based on design and airflow patterns, Types A1, A2, B1, and B2 are further subdivided.
Provide both personnel and product security.
Used extensively in microbiology, virology, and other applications involving low-risk agents.
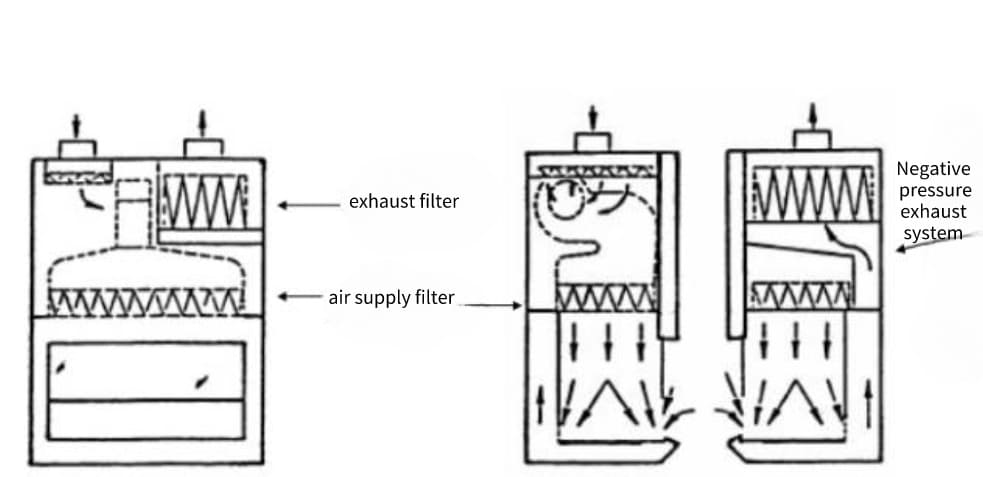
Class III Biosafety Cabinets
Cabinets with a viewing window that are completely enclosed and gas-tight.
Provide the highest level of protection when working with highly hazardous materials such as viruses and toxins.
Glove ports are used to ensure that no direct contact with the materials being handled occurs.
Key Practices When Using Biosafety Cabinets
- Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
To reduce the risk of exposure to biological agents, users must wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles.
- Cabinet Certification and Maintenance
Regular certification and maintenance are crucial to ensure the proper functioning of biosafety cabinets. This includes airflow verification, filter replacement, and compliance with relevant standards (e.g., NSF/ANSI 49).
- Aseptic Techniques
Adhering to aseptic techniques is essential to prevent contamination. This includes minimizing movement within the cabinet, avoiding unnecessary airflow disruptions, and using sterile tools and materials.
- Proper Work Practices
Work practices such as keeping the work surface uncluttered, maintaining a steady airflow, and using the back-third of the cabinet for activities contribute to an efficient and safe working environment.
- Airflow Patterns and Containment
Understanding the airflow patterns within the biosafety cabinet is crucial. Class II cabinets, for example, have inward airflow for personnel protection and downward laminar flow to maintain product protection.
- Avoiding Cross-Contamination
Proper separation of clean and contaminated materials within the cabinet is essential to prevent cross-contamination. Users should be aware of the airflow dynamics to strategically place materials.
- Emergency Procedures
It is critical to be familiar with emergency procedures, including shutdown protocols and alarm response. Regular training ensures that users can effectively respond in the event of an issue.
- Chemical Compatibility
When handling hazardous chemicals, users should be aware of the chemical compatibility of the materials with the cabinet and use appropriate containment strategies.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining detailed documentation of cabinet certification, maintenance, and user training is critical for regulatory compliance and accountability.
- Regular Training
Continuous training of laboratory personnel on the use of biosafety cabinets, proper techniques, and emergency procedures is critical to ensuring a safe working environment.

Diverse Applied Industries for Biosafety Cabinet Use
1. Microbiological Research
Biosafety cabinets play a pivotal role in microbiological research, providing a secure workspace for the handling of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. Class II BSCs, in particular, are widely used in microbiology laboratories for activities such as microbial culturing, specimen preparation, and virus manipulation.
2. Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratories
Biosafety cabinets are used in clinical and diagnostic laboratories to process and analyze patient samples. They ensure infectious agent containment, preventing pathogen release and cross-contamination during diagnostic procedures.
3. Pharmaceutical Research and Development
Biosafety cabinets are integral to pharmaceutical research and development, where the handling of biological materials is common. These cabinets provide a sterile environment for tasks such as cell culture work, preparation of vaccines, and the manipulation of genetically modified organisms.
4. Biotechnology and Genetic Research
Laboratories engaged in biotechnology and genetic research utilize biosafety cabinets for tasks involving the manipulation of DNA, RNA, and other genetic materials. Class II BSCs offer both personnel and product protection, making them suitable for these delicate procedures.
5. Animal Research Facilities
Biosafety cabinets find application in animal research facilities, where researchers work with laboratory animals and biological samples. Class III cabinets, with their enclosed design and glove ports, are particularly useful for handling highly hazardous materials in animal research.
6. Tissue Culture Work
Tissue culture work, essential in fields such as cell biology and regenerative medicine, requires a sterile environment to prevent contamination. Biosafety cabinets provide the necessary containment for activities like cell line maintenance, cell culture propagation, and tissue engineering.
7. Pathology Laboratories
Biosafety cabinets are used in pathology laboratories to ensure the safe processing and examination of pathological specimens. These cabinets aid in the protection of laboratory personnel while handling potentially infectious materials during diagnostic procedures.
8. Pharmacy Compounding
Biosafety cabinets are employed in pharmacy compounding to create sterile pharmaceutical preparations. This is critical in ensuring the safety of patients receiving customized medications, particularly those with compromised immune systems.
9. Teaching and Training Laboratories
Biosafety cabinets are valuable tools in educational settings, providing a safe environment for teaching and training activities. They allow students to learn and practice aseptic techniques and other laboratory procedures in a controlled and secure space.
10. Industrial Laboratories
Industries involved in the production of biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, and other biological products rely on biosafety cabinets for quality control, research, and development. These cabinets contribute to maintaining a sterile environment in industrial laboratories, ensuring the integrity of products.

Conclusion
Biosafety cabinets are essential tools in laboratories that work with hazardous materials because they provide a safe environment for research and experimentation. Following best practices in the use of biosafety cabinets ensures not only the safety of laboratory personnel but also the integrity of research results. Their numerous applications include microbiology, diagnostics, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and other fields. The applications of biosafety cabinets, whether in a research laboratory or an industrial facility, highlight their critical role in maintaining a secure and controlled environment for handling biological materials.


