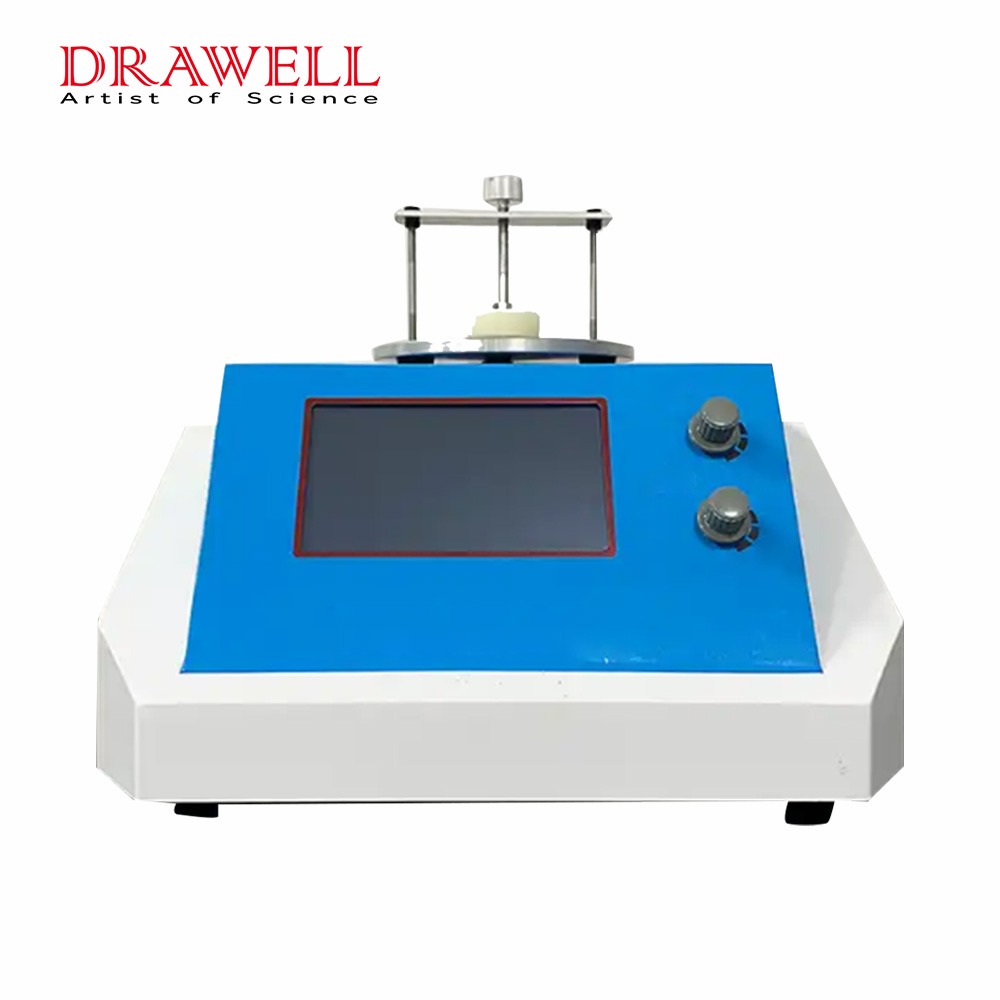
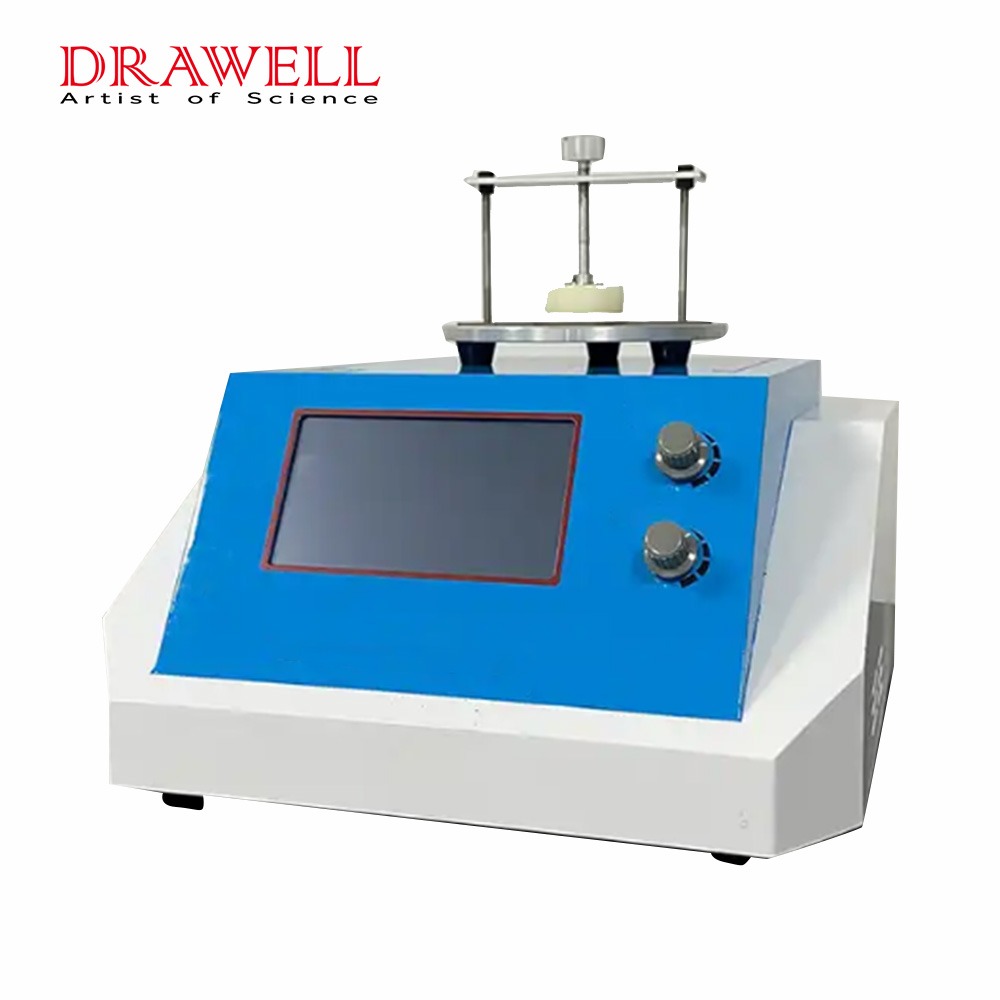
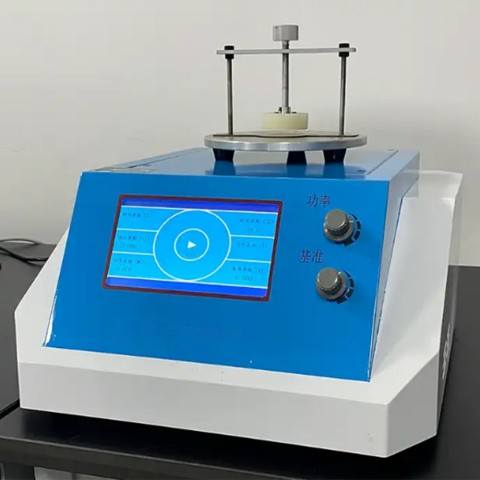
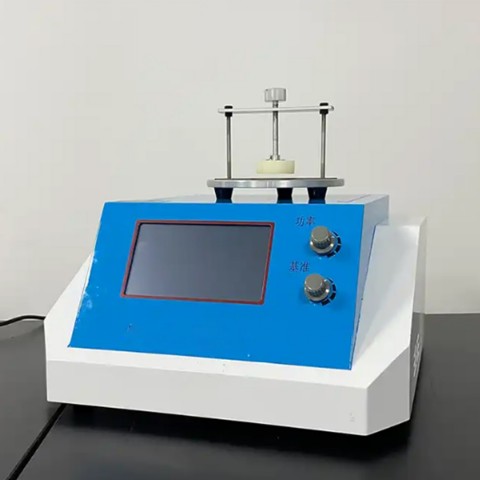
Transient Plane Heat Source Method Thermal Conductivity Meter BXT-DRS
The BXT-DRS rapid thermal conductivity tester is a thermal conductivity tester developed using transient planar heat source technology (TPS), which can be used to test the thermal conductivity of various materials. The transient plane heat source method is one of the medium-sized methods for studying the heat conduction performance, which brings the measurement technology to a whole new level. The ability to quickly and accurately measure thermal conductivity when researching materials provides great convenience for enterprise quality monitoring, material production, and laboratory research. The instrument is easy to operate, the method is simple and easy to understand, and it will not cause damage to the tested sample.

Working principle
Transient Planar Heat Source Technology (TPS) is a new method for measuring thermal conductivity, developed by Professor Silas Gustafsson of Chalmer University of Technology in Sweden on the basis of the hot wire method. The principle of measuring the thermophysical properties of materials is based on the transient temperature response generated by a step-heated disc-shaped heat source in an infinite medium. A flat probe is made of thermal resistance material, which serves as a heat source and temperature sensor at the same time.
The thermal resistance coefficient of the alloy is a linear relationship between temperature and resistance, that is, the heat loss can be known by understanding the change of resistance, which reflects the thermal conductivity of the sample. The probe of this method is a
continuous double helix structure sheet formed after etching treatment of a conductive alloy. The outer layer is a double-layer insulating protective layer with a very thin thickness. It makes the probe have a certain mechanical strength and keeps the distance between the sample and the sample. The electrical insulation.
During the test, the probe is placed in the middle of the sample for testing. When the current passes through the probe, a certain temperature rise is generated, and the generated heat is
simultaneously diffused to the samples on both sides of the probe. The speed of thermal diffusion depends on the thermal conductivity of the material. By recording the temperature and the response time of the probe, the thermal conductivity can be directly obtained from
the mathematical model.
Main features
- Fast and accurate: 5-160S can complete the test.
- Non-destructive testing: the sample is not damaged and can be reused.
- Simple sample preparation: no special requirements for sample size.
- A wide range of test objects: block solids, granular solids, liquids, powders, colloids, pastes can be tested.
- High flexibility: independent sample holder, detachable probe, flexible testing.
- User-friendly page, easy to operate: LCD touch screen display, easy to operate, easy tounderstand.
Superiority
- Instrument reference standard: ISO 22007-2 2008
- The test range is wide and the test performance is stable, which is at a level among similar domestic instruments;
- Direct measurement, the test time can be set about 5-160s, which can quickly and accurately measure the thermal conductivity, saving a lot of time;
- It will not be affected by contact thermal resistance like the static method;
- No special sample preparation is required, and there are no special requirements for the shape of the sample. The bulk solid only needs a relatively smooth sample surface and the length and width are at least twice the diameter of the probe;
- The non-destructive testing of samples means that the samples can be reused;
- The probe is designed with a double helix structure, combined with the exclusive mathematical model, and the core algorithm is used to analyze and calculate the data collected on the probe;
- The structure design of the sample table is ingenious, easy to operate, suitable for placing samples of different thicknesses, and at the same time simple and beautiful;
- The data acquisition on the probe uses an imported data acquisition chip. The high resolution of the chip can make the test results more accurate and reliable;
- The control system of the host uses an ARM microprocessor, which is faster than traditional microprocessors, improves the analysis and processing capabilities of the system, and makes the calculation results more accurate;
- The instrument can be used for the determination of thermophysical parameters such as block solids, paste solids, granular solids, colloids, liquids, powders, coatings, films, thermal insulation materials, etc.;
- Intelligent man-machine interface, color LCD screen display, touch screen control, convenient and simple operation;
- Powerful data processing capabilities. Highly automated computer data communication and report processing system.
Test object
Metals, ceramics, alloys, minerals, polymers, composite materials, paper, fabrics, foam plastics (insulation materials with flat surfaces, plates), mineral wool, cement walls, glass reinforced composite panels CRC, cement polystyrene panels, sandwiches Concrete, fiberglass composite panels, paper honeycomb panels, colloids, liquids, powders, granular and paste solids, etc., are tested in a wide range of objects.

Technical Parameters
| Test Range | 0.005-300W/(m*K) |
| Measuring temperature range | Room temperature— 130℃ |
| Probe diameter | No. 1 probe 7.5mm; No. 2 probe 15mm |
| Precision | ±3% |
| Repeatability error | ≤3% |
| Measure time | 5~160s |
| Power supply | AC 220V |
| Total power | ﹤ 500w |
| Sample temperature rise | ﹤ 15℃ |
| Test sample power P | No. 1 probe power 0<P<1w; No. 2 probe power 0<P<14w |
| Sample specifications | Single sample measured by probe No. 1 (15*15*3.75mm)A single sample measured by the No. 2 probe (30*30*7.5mm) |
| Note: The measurement of probe No. 1 is a low-conductivity material with a thinner thickness ≤0.2W/(m*K)). If the surface of the tested sample is smooth, flat and viscous, the samples canbe superimposed | |
Faster, simpler and more comprehensive than other methods
| Transientplanar heatsource method | Laser method | Hotline method | Protection plate method | |
| Measurement methods | Non-steady state method | Non-steady state method | Non-steady state method | Steady state method |
| Measurephysicalproperties | Get thermalconductivityand thermaldiffusivitydirectly | Simple sample preparation with specific requirements | Get thermal conductivity directly | Get thermal conductivity directly |
| Scope of application | Solid, liquid, powder, paste, colloid, granule | Solid | Solid, liquid | Solid |
| SamplePreparation | No special requirements, simple sample preparation | Complex sample preparation | Simple sample preparation with specific rquirements | Large sample size |
| Measurement accuracy | ±3%,prefera bly ± 0.5% | Preferably up to ± 10% | Preferably up to ± 5% | Preferably up to ±3% |
| Physicalmodel | Planar heat source contact measurement, as long as the limited surface contact is good | Non-contact heat source | Wire heat source, the wire model must be in good contact | Heat source contact type, need good surface contact |
| Thermalconductivityrange[w/(m*k)] | 0.005-300 | 10-500 | 0.005-10 | 0.005-5 |
| Measure time | 5-160S | A few minutes | Tens of minutes | Hours |
The operation method is simpleandeasytounderstand